Node Server Communication in Cooperative Multi-Node Storage

The rapid development of the digital age, especially the rise of data-intensive applications, cloud services, and artificial intelligence, has brought about significant changes in information technology. To meet these modern demands, organizations adopt multi-node storage systems where nodes distribute, organize, and store data.
In this context, node-server communication refers to the tangible protocols, mechanisms, and frameworks that enable different storage nodes to communicate with each other’s servers. Its goal is to create harmony in the system, data consistency, and provide users with reliable and secure storage.
This article explains how communication between nodes and servers can be done. What protocols and security principles are used in this? Furthermore, the research highlights the challenges it faces and the possibilities for future research and development.
How Cooperative Multi-Node Storage Powers TeraBox Performance
Node Server Communication in Cooperative Multi-Node Storage is linked to TeraBox because it distributes and syncs files across multiple node servers. Each node communicates with others to ensure data availability and redundancy. This system allows TeraBox to provide stable access to large files and old versions. Such cooperative node communication makes TeraBox fast, reliable, and scalable.
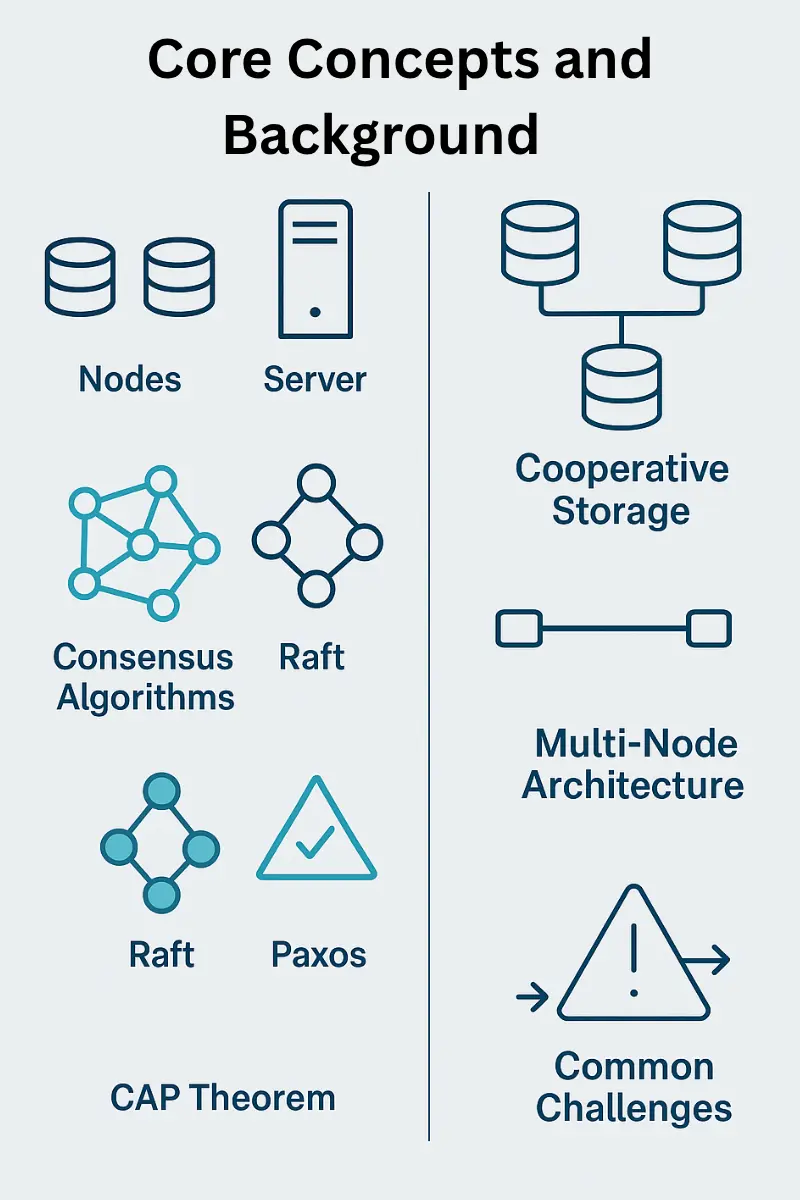
Core Concepts and Background
The basic concepts and background between the node and server in collaborative and multi-node storage systems are explained with the following explanation.
Core concepts
Here are the core concepts for understanding and designing a multi-node storage system.
Nodes: In a distributed storage system, independent computing units that store a portion of the data. In addition to storage, their function is to communicate, transfer data, and synchronize with other nodes in the system.
Server: A coordinating component that monitors and manages a network of nodes. It can be a central server or a distributed system where nodes operate autonomously.
Data Consistency: Data consistency ensures all nodes have an updated, uniform copy, which is challenging across multiple nodes.
Consensus Algorithms: Consensus logarithm helps nodes in a distributed system agree on data state despite network problems or failures
Raft: This algorithm selects a leader from among the nodes and keeps track of changes in the system through log replication to maintain data consistency.
Paxos: It is a robust and complex algorithm used in distributed systems to achieve consensus despite network fragmentation.
CAP Theorem: This theory states that a distributed system can ensure only two of three properties: availability, partition tolerance, and consistency, since partitions are inevitable.
Background
Below is the background of cooperative storage cloud and multi-node servers.
Cooperative Storage: This is a storage model where data is stored across multiple nodes, which collectively organize and store the data, have relatively little reliance on a central server.
Multi-Node Architecture: This is a server design that includes multiple nodes in a single physical chassis. This design is suitable for high-performance computing or cloud applications.
Network Communication: These are a means of accelerating network speeds between InfiniBand or Ethernet nodes, which enables data transfer and synchronization.
Common Challenges: Problems faced by distributed systems include hardware failures, software bugs, and network outages. The goal of server communication is to maintain data and availability despite these failures.
Node-Server Communication in Cooperative and Multi-Node Storage Systems
The prominent types of technical purposes for which connections are made between nodes and servers are as follows:

Node Performance Status Reports
Nodes periodically send small messages called heartbeat messages to provide their health, CPU usage status, and other important information to the server or other nodes. The purpose of this is to inform the system that a particular node is active and working. If a node does not send a heartbeat message within a specified time, the system considers it a failure and immediately reacts appropriately.
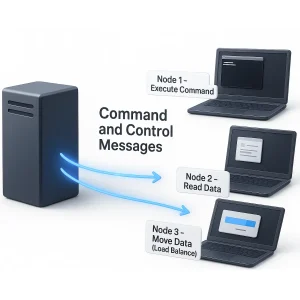
Command and Control Messages
These messages are sent by the server to instruct nodes to perform specific tasks. They are essential for keeping the overall operation of the system organized and robust. For example, the server can instruct a node to write or read data, or to move data to optimize storage. These messages can be used as load balancing to distribute the workload so that the system performance is maintained.

Coordination Messages
For data consistency, these messages are exchanged between nodes to agree on a decision or a shared state. They are more important when multiple nodes are modifying and accessing the same data. Consensus algorithms such as Raft and Paxos are used for this purpose, which enable processes such as leadership election or lock replication. In this way, even in the event of partial failures, the system maintains a unified and consistent view of the data.
Acknowledgement Messages
Short signals called acknowledgement messages are sent to the receiving node or server to confirm the successful receipt of a previous message or instruction. These messages ensure that the data has been safely delivered and correctly executed. ACKs play an important role in reliable communication protocols like TCP because they ensure data integrity and protect against loss. If an ACK is not received within a specified time, the message is retransmitted. This process is part of systems like Handshaking and Reliability Protocols.


Failure Notices/ Error or Fault
Failure notifications are messages that are sent in the event of unexpected events such as node offline, network breakdown, or software failure. These messages are sent to provide timely notification of system failure or abnormal conditions. Or so that recovery and replacement processes can be initiated in a timely manner. Upon their receipt, automatic reactions such as removing the failed node from the list or transferring its work to other nodes are implemented. These messages maintain resiliency and high availability and make fault tolerance effective. These concepts include error reporting verb over and system resilience.
Protocols & Communication Channels for Node Server Communication
| Protocol / Mechanism | Description | Key Use Case / Benefits |
| HTTP / REST APIs | A widely adopted, integration-friendly standard for client-server communication, primarily utilizing JSON or XML data formats. | General-purpose web services, stateless operations, high compatibility, and ease of integration across different platforms. |
| gRPC | A modern, high-performance Inter-Process Communication (IPC) framework based on HTTP/2, utilizing efficient binary serialization (Protocol Buffers). | Low-latency microservices communication, efficient data exchange, and high throughput in distributed systems. |
| WebSockets / TCP | Provides full-duplex (two-way) communication channels over a single, long-lived TCP connection. | Real-time applications, live updates, gaming, and persistent connections where immediate response is needed. |
| TLS/SSL Encryption | Cryptographic protocols designed to secure data transmission, ensuring privacy and data integrity between nodes and servers. | Essential for securing sensitive data in transit, preventing eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. |
| Authentication & Authorization | Mechanisms for verifying the identity of communication endpoints and controlling their access permissions within the system. | System security, ensuring only trusted nodes can access specific resources or execute commands. |

Synchronization & Coordination
State synchronization is essential to maintain consistency between nodes. For this purpose, the server exchanges regular health reports and acknowledgement messages so that consistency is not affected. Load balancing algorithms such as hash based, Round Robin, Distribution and weighted balancing distribute the load appropriately so that the node is not under too much stress.
Security, Trust and Encryption Mechanisms
In a distributed system, Node Server Communication relies on security, trust, and encryption for secure and reliable data exchange. To maintain confidentiality and prevent theft and intrusion, data transmitted in the system is protected by TLS/SSL encryption. Authentication allows only authorized nodes to join the network and then authorizes the execution of actions by authenticated nodes based on the authorization principle. Hashes or digital signatures are used to prevent unauthorized changes and to ensure data integrity. Comprehensive audit logging keeps a record of all activity to ensure system resilience.


Scalability
Scalability is a key feature of an efficient distributed system that handles the increasing workload by using additional nodes. True linear scalability means that each new node can be added to the system in a proportional manner without interrupting the service. This capability ensures fast response and reliable performance.
In large networks, specialized protocols such as Partition Aware Routing and Distributed Hash Tables (DHTs) manage data efficiently. These methods reduce unnecessary load by fairly distributing data and responsibilities among nodes. Horizontal scaling is possible with this approach to create high availability and automatic growth.
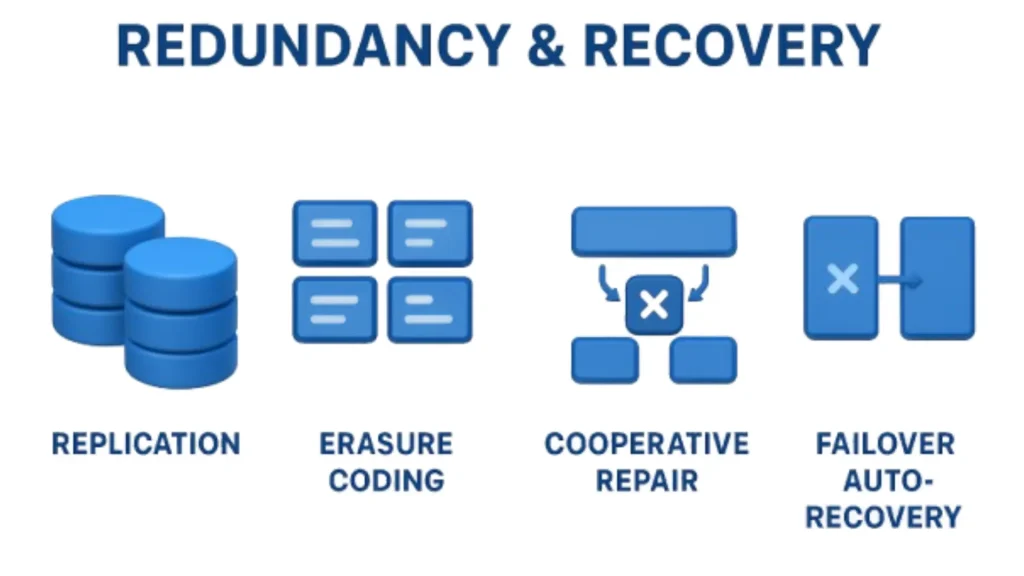
Redundancy & Recovery
Replacement and recovery ensure data availability and resilience in the system. Replication provides multiple points of data safety while Erasure coding provides secure storage in a small space. In Cooperative Repair, failed nodes take partial fragments from healthy nodes and reconstruct the lost data.
For system continuity, failover mechanisms immediately transfer the work of a failed node to the active nodes. These methods eliminate single points of failure and improve performance by reducing downtime. Similarly, the system ensures high availability and auto recovery.
Emerging Concepts
New techniques and architectures are emerging in modern distributed storage systems that further improve Node Server Communication performance and scalability. The most prominent of these concepts is described below.

Software-Defined Storage – SDS
In the SDS model, storage is abstracted away from hardware and managed by software. Each storage resource is API-driven, so this model improves node-server communication. This enables dynamic provisioning, which increases scalability, automation, and policy-based control in cloud infrastructure.
Converged Storage
Converged storage combines computing and storage resources on a single platform, making this architecture faster and more efficient for Node Server Communication. This results in lower latency and higher throughput, which are beneficial in HPC and edge computing environments.
High-Performance Storage Systems
In HPC environments, storage systems such as GPFS, Lustre, and BeeGFS improve node-server communication through high-speed networking such as InfiniBand, RDMA, and metadata caching.
To further enhance Node Server Communication performance, efficient message batching and caching strategies are used to reduce latency and speed up data exchange. These optimizations help increase throughput, maintain reliability, and ensure the system remains continuously operational with minimal downtime.
Data Types and Storage Models
Node Server Communication depends on the storage model used, which includes the following types.
H4 Block Storage: It provides direct block-level access and is latency-sensitive.
File Storage: It is based on a hierarchical file system and stores detailed metadata information with each file.
Object Storage: It stores data as objects, provides access to data through REST APIs, and is highly scalable, as offered by some online storage services.
Since each storage model is different, the nature of communication, messaging protocols, and synchronization associated with them also varies.
Autonomic Optimization / ML Integration
Modern research is using reinforcement learning-based models, such as RL storage, that automatically optimize resource allocation and data placement. These systems self-monitor and optimize their policies to reduce latency and increase throughput.
Latency and Energy Efficiency
Communication overhead and repeated synchronization affect energy consumption. Energy-aware scheduling and adaptive message throttling reduce latency by 30-40%. Low encryption and overhead in node-server communication and efficient routing are important for saving energy.
Storage Hierarchy & Tiered Storage
Modern systems store frequently accessed and rarely accessed data at different levels such as HDDs, SSDs, NVMe, and cloud tiers. Node Server Communication manages data movement between these hierarchies using a data tiering algorithm.
Storage Resource Management Tools / Middleware
Storage Resource Management (SRM) tools, such as Ceph Dashboard, OpenStack Cinder, or vSAN Manager, monitor the health, quota, and performance of nodes through communication channels. This middleware automates message routing, alerts, and performance tuning within the system.
Real-world Examples & References
- Google File System (GFS) — Used for big data storage at Google. Ref: Ghemawat et al., The Google File System, 2003
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) — Used for big data processing at Facebook and Yahoo. Ref: Shvachko, HDFS Architecture, 2010.
- Ceph Storage — Scalable and reliable storage in cloud platforms. Ref: Weil et al., Ceph: A Scalable, High-Performance Distributed File System, 2006.
Challenges & Limitations
The following challenges and restrictions directly impact the performance and stability of distributed storage systems.

Common Security Threats and Risks
Strong encryption such as TLS/SSL and appropriate authentication mechanisms are essential. Their absence exposes the system to security issues such as intrusion, unauthorized access, and data loss. Strict security protocols must be implemented across all communication channels to maintain data confidentiality and system integrity.

Synchronization complexity
Maintaining unified and consistent data across multiple, independently operating nodes is a major challenge. Consensus algorithms and synchronization protocols are used for this. However, they also increase system complexity and make development more difficult.

Node reliability
In a distributed system, nodes can suddenly shut down due to hardware failures, software errors, or network problems. A single unstable node can affect the integrity of the entire system and data. Therefore, it is necessary to implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to maintain system resilience and high availability.

Network Latency
Geographic distance is a fundamental physical limitation that slows down the speed of communication between distributed nodes and servers. This latency affects the overall performance of the system, especially where real-time processing or rapid consensus is required. Therefore, sophisticated network optimization strategies and careful architectural design are essential.

Overhead
Essential processes such as connectivity, synchronization, and security consume additional network bandwidth and CPU cycles. This affects the overall performance of the system and the resources of the underlying application. To mitigate these problems, it is necessary to adopt better message formats and appropriate batching strategies.
Research and Future Directions
These modern research trends enable distributed systems to operate faster, more securely, and more autonomously. Prominent examples are given below.

Low latency co-operative communication protocols
Future research aims to develop protocols that reduce latency through better connectivity between nodes. These protocols allow nodes to communicate with each other without relying on a central server, creating a faster and more secure system.
Privacy-Focused Models like Homomorphic Encryption & Secure Multi-Party Computation
Future systems are using advanced encryption methods to maintain data privacy and security in Node Server Communication. Homomorphic Encryption processes data in an encrypted state to ensure confidentiality. This method, combined with secure multiparty computation, enables computation between different methods without the direct exchange of sensitive data.
Improved Coding Techniques that Minimize Redundancy & Maximize Reliability
New coding techniques use less storage than older replication techniques and maintain data reliability. These modern methods enable the fastest recovery in the event of a node failure.
Edge + Cooperative Storage Combination
Edge computing is being integrated with cooperative storage in modern systems. This approach reduces latency and communication overhead, making it especially effective for IOT and real-time applications. The aim is to significantly reduce the distance from the central data center by storing data on nodes closer to the end user.
AI-Driven Orchestration Systems
Upcoming systems will include AI-based orchestration mechanisms capable of more efficient, responsive, and automated recovery without human intervention. These systems are capable of monitoring network traffic, load balancing, and automatically distributing resources.
Conclusion:
The foundation of multi-node and private storage is efficient Node Server Communication. These mechanisms combine security synchronization and load balancing and data recovery, which makes the system reliable. Software-defined storage (SDS) and machine learning (ML) are making these systems more powerful and efficient. Future research is making these models more autonomous, energy-efficient and secure, which will promote scale-appeal and reliable distributed computing environments in the future.
